Universal life insurance is a versatile and adaptable form of permanent life insurance that combines a death benefit with a savings component. This insurance product stands out due to its flexibility in premium payments and the potential for cash value accumulation, making it an appealing option for many. In this article, Familysitescatalog will explore the key features, advantages, disadvantages, types, and suitability of universal life insurance, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this insurance solution.
Key Features of Universal Life Insurance
One of the primary attractions of universal life insurance is its flexible premiums. Unlike traditional whole life insurance, where premiums are fixed, universal life insurance allows policyholders to adjust the amount and timing of their premium payments. This flexibility means that as long as there is sufficient cash value in the policy to cover the cost of insurance and any administrative fees, premiums can be increased, decreased, or even skipped entirely. This adaptability can be particularly beneficial for individuals whose income may fluctuate over time.
Another significant feature is cash value accumulation. A portion of the premiums paid into a universal life insurance policy goes into a cash value account, which grows over time. The growth rate is typically linked to a financial index or determined by a declared interest rate from the insurance company. This cash value can be accessed through loans or withdrawals, providing a valuable financial resource for policyholders.

Universal life insurance also offers an adjustable death benefit. Policyholders can increase or decrease the death benefit within certain limits without the need to purchase a new policy. However, increasing the death benefit may require additional underwriting to ensure the policyholder’s insurability.
Policyholders have the option to take out loans and withdrawals against the cash value. Loans accrue interest and any unpaid balance will reduce the death benefit. Similarly, partial withdrawals will decrease both the cash value and the death benefit, offering flexibility but also requiring careful management.
The interest rates and performance of the cash value component can vary. While universal life insurance typically includes a guaranteed minimum interest rate, the actual interest credited can fluctuate based on market conditions or the insurer’s performance. This variability can impact the overall growth of the cash value.
Advantages of Universal Life Insurance
The flexibility in premiums and death benefits is a significant advantage of universal life insurance. This adaptability allows policyholders to adjust their coverage and payments in response to changing financial circumstances, making it a versatile financial tool.
Another advantage is the potential for higher returns on the cash value. Depending on the type of universal life insurance and the performance of the underlying investments, the cash value may grow at a rate higher than that of traditional whole life insurance. This potential for growth can be an attractive feature for those looking to build a significant cash value over time.
Universal life insurance also offers tax benefits. The cash value grows on a tax-deferred basis, meaning that policyholders do not pay taxes on the growth until they withdraw it. Additionally, the death benefit is generally paid out tax-free to beneficiaries, providing a tax-efficient way to transfer wealth.

Disadvantages of Universal Life Insurance
Despite its many advantages, universal life insurance also has disadvantages. One of the main drawbacks is its complexity. The various options for adjusting premiums, death benefits, and investment choices can make these policies difficult to understand and manage without professional assistance.
Another potential downside is the market risk associated with certain types of universal life insurance. For policies where the cash value is tied to market performance, such as Indexed Universal Life (IUL) or Variable Universal Life (VUL), poor market conditions can negatively impact the cash value. This risk can increase the likelihood of the policy lapsing if the cash value is insufficient to cover the cost of insurance.
Additionally, universal life insurance policies often come with higher fees and charges compared to other types of life insurance. These fees can include administrative costs, mortality charges, and fees for managing the cash value investments. These charges can erode the cash value, especially in the early years of the policy.
Types of Universal Life Insurance
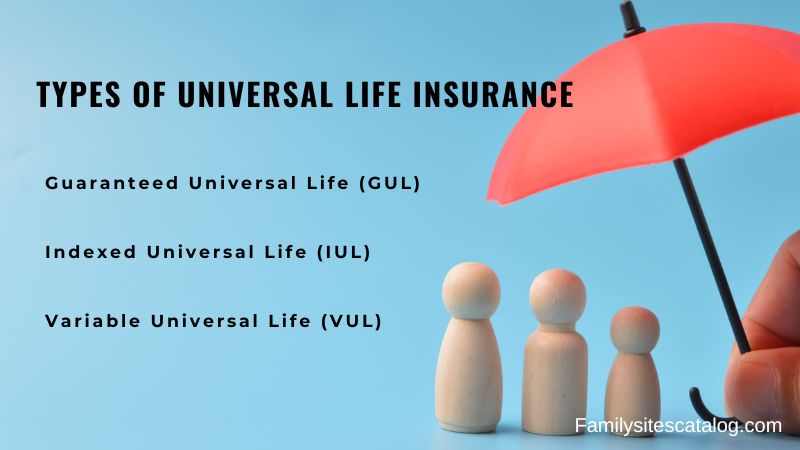
There are several types of universal life insurance, each with unique features and benefits:
- Guaranteed Universal Life (GUL): This type offers a guaranteed death benefit with typically lower premiums but minimal cash value accumulation. It is ideal for those primarily seeking a guaranteed death benefit without a focus on cash value growth.
- Indexed Universal Life (IUL): The cash value growth in IUL policies is linked to a stock market index, such as the S&P 500. This provides the potential for higher returns while offering some protection against market downturns through caps and floors on the interest credited.
- Variable Universal Life (VUL): VUL policies allow policyholders to allocate their cash value to various investment options, similar to mutual funds. This offers the potential for significant cash value growth but also comes with higher risk due to market fluctuations.
Suitability of Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is suitable for individuals who seek lifelong coverage with the flexibility to adjust premiums and death benefits. It is particularly beneficial for those who anticipate changes in their financial situation over time and want the ability to modify their insurance accordingly.
This type of insurance is also ideal for those interested in accumulating cash value that can be used for future financial needs, such as supplementing retirement income or funding major expenses. The tax-deferred growth of the cash value and the tax-free death benefit make it a tax-efficient financial planning tool.
However, universal life insurance is not suitable for everyone. The complexity of these policies requires a certain level of understanding and financial literacy. Additionally, those who are risk-averse may find the market-linked variations, like IUL and VUL, too volatile for their comfort.
Conclusion
Universal life insurance offers a unique combination of flexibility, potential for cash value growth, and lifelong coverage. Its ability to adapt to changing financial circumstances and provide a tax-efficient way to accumulate and transfer wealth makes it an attractive option for many. However, the complexity, market risks, and higher fees associated with these policies necessitate careful consideration and, often, professional guidance.
By understanding the key features, advantages, disadvantages, and types of universal life insurance, individuals can make informed decisions about whether this insurance product aligns with their financial goals and needs. Consulting with a financial advisor or insurance specialist can provide additional insights and help navigate the intricacies of universal life insurance, ensuring that it serves as an effective component of a comprehensive financial plan.